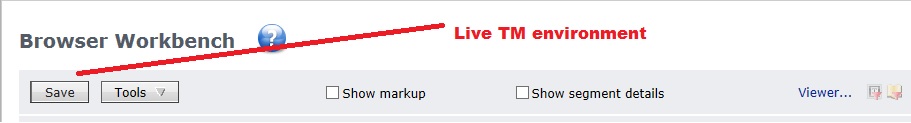
The fastest way is to open any file or Task in
Browser Workbench. If you see only a
Save button, you are on a
live-TM environment. In a live-TM mode, every time a translation is saved with the
Save button or through the
Save Workflow step and also every time a Return package is imported successfully, the Translation Memory associated with this file or project will be updated.
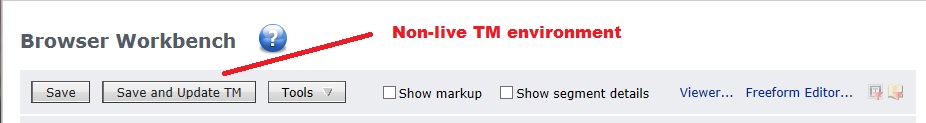
If you see 2 buttons in Browser Workbench: one called
Save and the other called
Save and update TM, you are in a
non-live TM environment.
In this environment (
non Live TM), clicking on
Save will save your translation to a
WorldServer cache, but it will
not update the TM. A
Save step in the Workflow can be configured to update the TM or to not update it. Also: when importing a Return package to a WorldServer non live-TM environment, the translator will have the option to update the TM or only update the cache with the translation. A non live-TM environment offers more control about the quality of the translated content to be included in the TM because you can determine at what stage of your Workflow the translation should update the TM.
More information about the difference between
live TM mode and
non-live TM mode can be found
here.




